|

|
|
|
Early development of the cardiac musculature
|
|
|
|
The cardiac musculature stem from mesenchymal material that forms the cardiogenic plate in the early development before the prechordal plate 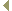 8 8 . .
This mesenchyme consists of a connected group of cuboid cells in the ventral mesoderm.
|
|
|
| Fig. 19 - Embryo in stage 8, ca. 23 days |
|
Legend |
A
B
C
D
E
|
Section at the level of the prechordal plate
Section at the level of the notochord plate
Section at the level of the notochordal process
Section at the level of the primitive streak
Section at the level of the cloacal membrane |
|
|
|
Fig. 19
The left diagram shows an overview of the embryonic plate In the middle a lateral view of the same embryo is shown.
On the right, the cross sections are shown that correspond to the levels indicated with the capital letters. At this stage the material for the cardiac anlage, the myocardial plate or cardiogenic plate, lies cranial to the prechordal plate.
|
Fig. 20 - Embryo in stage 9, ca. 25 days
(longitudinal section) |
|
Legend |
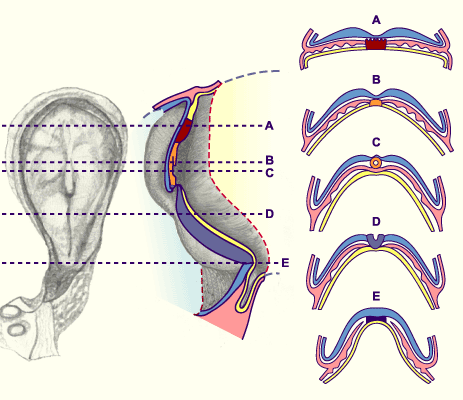
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
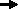 |
Cardiac tube
Pericardial cavity
Umbilical vesicle
Amniotic cavity
Hypoblast
Neural plate
Extraembryonic mesoderm
Cranial eminence
Position of the material for the diaphragm |
|
|
|
Fig. 20
The embryo is shown with its dorsally lying amniotic cavity and the ventrally lying umbilical vesicle. Due to the folding over of the embryos, the cardiac anlage and the material for the diaphragm undergo a rotation around 180 degrees. The pericardial cavity develops above the cardiac anlage. A part of the material for forming the diaphragm lies on the cranial side of the cardiac anlage. Furthermore, the notochord plate is visible. It replaces the hypoblast in the medial part.
|
Fig. 21 - Embryo in stage 10, ca. 28 days
(longitudinal section) |
|
Legend |
1
2
3
4
5
6a
6b
6c
7
8
 |
Cardiac tube
Pericardial cavity
Umbilical vesicle
Amniotic cavity
Endoderm
Cranial neuropore
Neural tube
Caudal neuropore
Extraembryonic mesoderm
Cranial eminence
Position of the material for the diaphragm |
|
|
|
Fig. 21
The embryo begins to fold over cranially and caudally. This is why the cardiac anlage and the material destined for the diaphragm undergo a rotation of 180 degrees. The pericardial cavity, which first develops above the cardiac anlage, comes to lie ventrally. Further on, in stage 10 the closure of the neural tube begins. In its cranial and caudal parts, though, it remains open (neuroporus cranialis and caudalis). The notochordal plate has also separated from the endoderm and formed the definitive notochord.
|
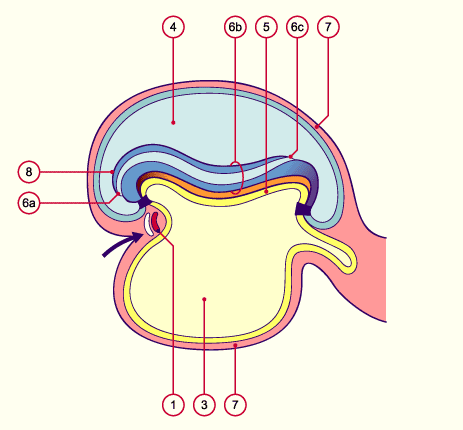
Fig. 22 - Embryo in stage 11, ca. 29 days
(longitudinal section) |
|
Legend |
1
2
3
4
5
6a
6b
6c
7
8
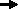 |
Cardiac tube
Pericardial cavity
Umbilical vesicle
Amniotic cavity
Endoderm
Cranial neuropore
Neural tube
Caudal neuropore
Extraembryonic mesoderm
Cranial eminence
Position of the material for the diaphragm |
|
|
|
Fig. 22
The rotation of the cardiac anlage is complete; the pericardial cavity now lies ventral to the cardiac anlage. With the folding, the future intestines have arranged themselves into three sections: foregut, midgut and endgut. The neural tube is closed cranially. The diaphragm anlage, the transverse septum, now lies between the cardiac anlage and the umbilical vesicle, in front of the liver bud. With the folding over, the allantoic stalk is now found on the ventral side of the embryo. In this stage the oropharyngeal membrane is already open. A communication thus exists between the intestines and the amniotic cavity (not shown here).
|
Fig. 23 - Embryo in stage 12, ca. 30 days
(longitudinal section) |
|
Legend |
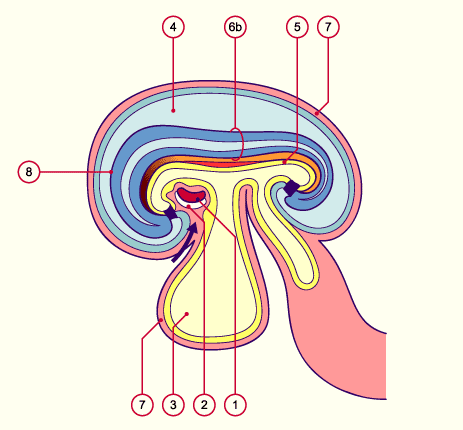
1
2
3
4
5
6b
7
8
 |
Cardiac tube
Pericardial cavity
Umbilical vesicle
Amniotic cavity
Endoderm
Neural tube
Extraembryonic mesoderm
Cranial eminence
Position of the material for the diaphragm |
|
|
|
Fig. 23
The folding over of the embryo is almost complete. Through the massive expansion of the brain the navel region with the umbilical vesicle and the allantois in the allantoic stalk become more compressed. Between the endoderm and the notochord the dorsal aorta has fused in the middle section. Above and below it is still paired.
|
|
|

